|
 |
My book, Weeb Economy came out in March, but only in Japanese. Half of the book was a series of translated posts from my blog, so those are already in English. The other half was a new part that I wrote in English and had translated into Japanese by my excellent translator, Kataoka Hirohito. So while I’ll eventually republish the whole book in English, what I can do right now is to publish my English-language first draft as a series of posts on this blog.
The first installment was entitled “I Want the Japanese Future Back!”. In that post, I explained why Japan now finds itself in the position of a developing country, playing catch-up with other countries. This means Japan needs to experiment with bold new strategies and development models, as it did in ages past.
In this second installment, I suggest one such experiment: a huge increase in a kind of investment called greenfield FDI. I discuss:
How Japan is already benefitting from greenfield FDI in a few places
Why greenfield FDI (a foreign company building a factory or research center in Japan) is so much more important and useful than other kinds of FDI like mergers and acquisitions
Why Japan needs to export a lot more to other countries, and how greenfield FDI can help do that
How Japan can start to welcome more greenfield FDI
Why Japan is an attractive destination for international investment
The Kumamoto miracle points the way
The semiconductor industry is probably the most important industry in the world. Computer chips are absolutely essential to every high-value product in a modern economy — autos, rockets, appliances, machinery, everything. They’re also of crucial military importance, in an age where precision weaponry rules the battlefield. And they’re of core importance to emerging technologies like AI — whose vast computational resources require enormous data centers — and biotech.
As a result, it’s no wonder that the world’s major economies have been fighting over the semiconductor industry for generations. In the early days, the U.S. and Japan were the clear leaders. Much of the industry involves the design of semiconductors and the production of specialized tools and materials, and in these upstream parts of the industry the U.S. and Japan are still strong. But in the most important downstream part of the process — the actual fabrication of the most advanced chips — both the U.S. and Japan have lost their lead to Taiwan:
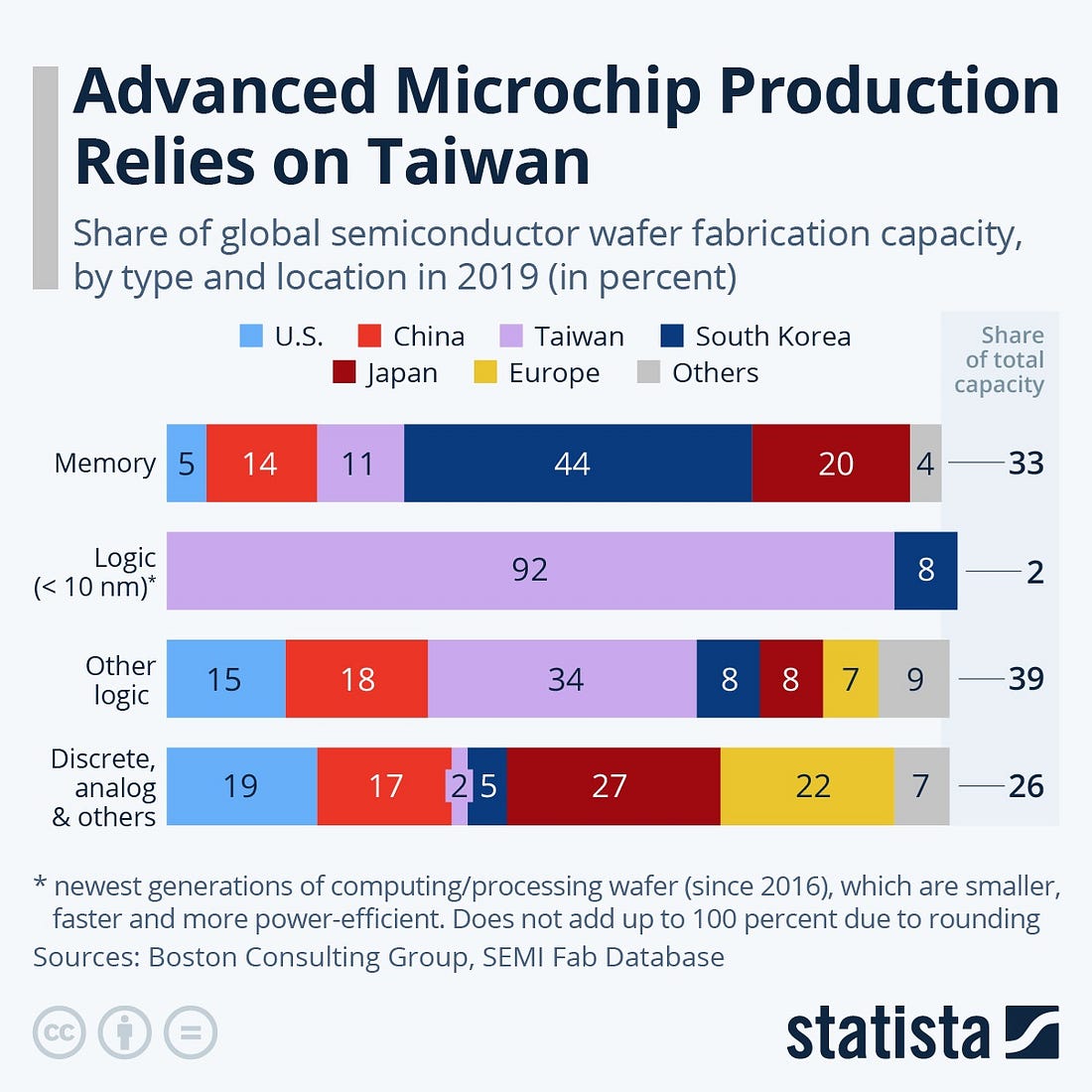 |
Specifically, they have lost their lead to one remarkable Taiwanese company: Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company. TSMC are essentially the world’s greatest machinists. Other companies design the chips, and other companies create the (incredibly advanced) machine tools that make the chips. What TSMC does is to buy the tools, and then use the tools with incredible ingenuity and efficiency to make someone else’s chips designs into reality. They pioneered this “pure-play foundry” business model, and it has made them rich — and it has allowed Taiwan to outcompete the chipmaking industries of every other country on the planet.
Since the pandemic, the global battle to win semiconductor market share has intensified, due to the advent of AI and to the geopolitical competition between China and the democratic countries. Japan, like many countries, is trying to build its own foundry business, in the form of Rapidus, a joint venture between a bunch of Japanese companies that’s also getting some help from IBM. But — also like in the U.S. there’s also a second, parallel effort afoot. Japan is building chips for TSMC.
In late 2021, TSMC created a Japanese subsidiary called Japan Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing (JASM), and started building two fabs in Kumamoto prefecture. Sony and Denso pitched in to help. So did the Japanese government, providing billions of dollars in subsidies and offering TSMC logistical assistance in finding local workers and ensuring adequate water and other infrastructure. The first plant was completed very quickly, and opened in February 2024; the second is expected to open in 2025. Now TSMC is considering a third fab in Kumamoto, producing even more advanced chips, to be opened in 2030.
Observers have been impressed with the speed with which the fab was built, comparing it favorably to TSMC’s plant in America, which initially suffered delays. TSMC credited the successful construction to a variety of local supporting institutions — “suppliers, customers, business partners, government and academia.” TSMC’s founder Morris Chang, who once poked fun at Japan for the slow speed of its business dealings, has now become a true believer in the revival of the country’s chip industry. At the opening of the first TSMC plant in Kumamoto, Chang predicted a “renaissance of semiconductors” in Japan.
And Japan isn’t stopping with TSMC. Micron, an American chip company, is building a fab in Hiroshima, bringing some of its best technology into the country. Samsung is building a semiconductor development center in Yokohama. Both of these investments are being done with significant help from the Japanese government, and involve cooperation with Japanese companies and universities.
These investments by foreign companies aren’t Japan’s only strategy for reviving its semiconductor industry — they coexist alongside homegrown efforts like Rapidus, as well as Japan’s upstream efforts in the chipmaking tool and materials industries. But they represent a crucial addition to the purely indigenous efforts. This is an example of multi-strategy development at work.
But it’s far from the only such example.
A school of AI fish
The artificial intelligence boom is the most important trend in the software industry right now. Whether this remains true in future years remains to be seen, of course, but the capabilities of large language models like ChatGPT, AI art software like Midjourney, and computer vision systems are undeniable. Even if there’s a bubble and bust in the field at some point — as there was with dot-com companies in 2000 — AI is going to be important in the long term.
Japan largely missed out on the internet software boom — the country has no internationally dominant consumer internet giants like Google or Facebook, and its B2B software industry was hampered by Japanese companies’ slowness to adopt IT solutions in past decades. But the AI age is a new dawn, and Japan has another shot at building a powerful software industry.
At the time of this writing, one of the most interesting AI startups in Japan is