|
The dawn of the posthuman age
Between new technology and low fertility, our existence as a species is not going to be the same.
 |
“Can you picture what we’ll be/ So limitless and free/ Desperately in need of some stranger’s hand” — The Doors
In the 1990s and 2000s, a lot of science fiction focused on what Vernor Vinge called “the Singularity” — an acceleration of technological progress so dramatic that it would leave human existence utterly transformed in ways that it would be impossible to predict in advance. Vinge believed that the Singularity would result from rapidly self-improving AI, while Ray Kurzweil associated it with personality upload. But both believed that something big was on the way.
In the late 2000s and 2010s, as productivity growth slowed down, these wild expectations got tempered a bit. Cory Doctorow and Charles Stross poked fun at the idea of the Singularity as “the rapture of the nerds”. And some bloggers, like Brad DeLong and Cosma Shalizi, began to argue that the true Singularity was in the past, when the Industrial Revolution freed us from the constraints of daily hunger and scarcity. Here’s Shalizi:
The Singularity has happened; we call it "the industrial revolution" or "the long nineteenth century". It was over by the close of 1918…Exponential yet basically unpredictable growth of technology, rendering long-term extrapolation impossible (even when attempted by geniuses)? Check…Massive, profoundly dis-orienting transformation in the life of humanity, extending to our ecology, mentality and social organization? Check…Embrace of the fusion of humanity and machines? Check…Creation of vast, inhuman distributed systems of information-processing, communication and control, "the coldest of all cold monsters"? Check; we call them "the self-regulating market system" and "modern bureaucracies" (public or private), and they treat men and women, even those whose minds and bodies instantiate them, like straw dogs…An implacable drive on the part of those networks to expand, to entrain more and more of the world within their own sphere? Check…
Why, then, since the Singularity is so plainly, even intrusively, visible in our past, does science fiction persist in placing a pale mirage of it in our future? Perhaps: the owl of Minerva flies at dusk; and we are in the late afternoon, fitfully dreaming of the half-glimpsed events of the day, waiting for the stars to come out.
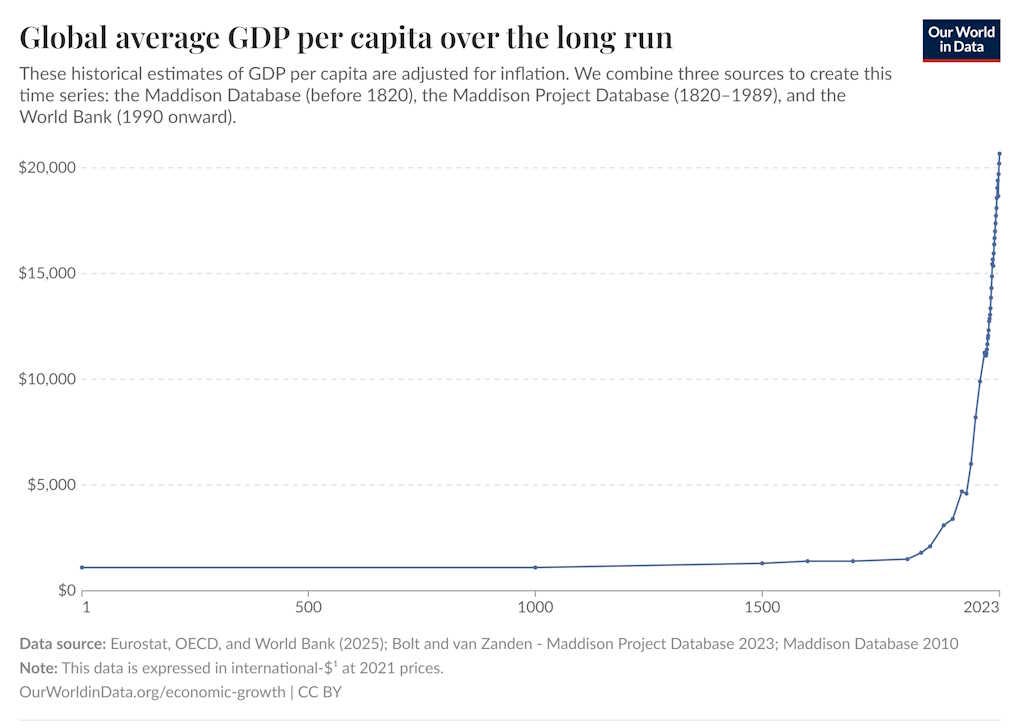
I agree that the Industrial Revolution represented an abrupt, unprecedented, and utterly transformational change in the nature of human life. Human life until the late 1800s had been defined by a constant desperate struggle against material poverty, with even the bounty of the agricultural age running up against Malthusian constraints. Suddenly, in just a few decades, humans in developed countries were fed, clothed, and housed, and had leisure time to discover who they really wanted to be. It was by far the most important thing that had ever happened to our species:
And it’s important to note that this transformation wasn’t just a result of technology giving humans more stuff. It depended crucially on reductions in human fertility. As Brad DeLong documents in his excellent book Slouching Towards Utopia, after a few decades, the Industrial Revolution prompted humans to start having fewer children, which prevented the bounty of industrial technology from eventually being dissipated by the old Malthusian constraints.
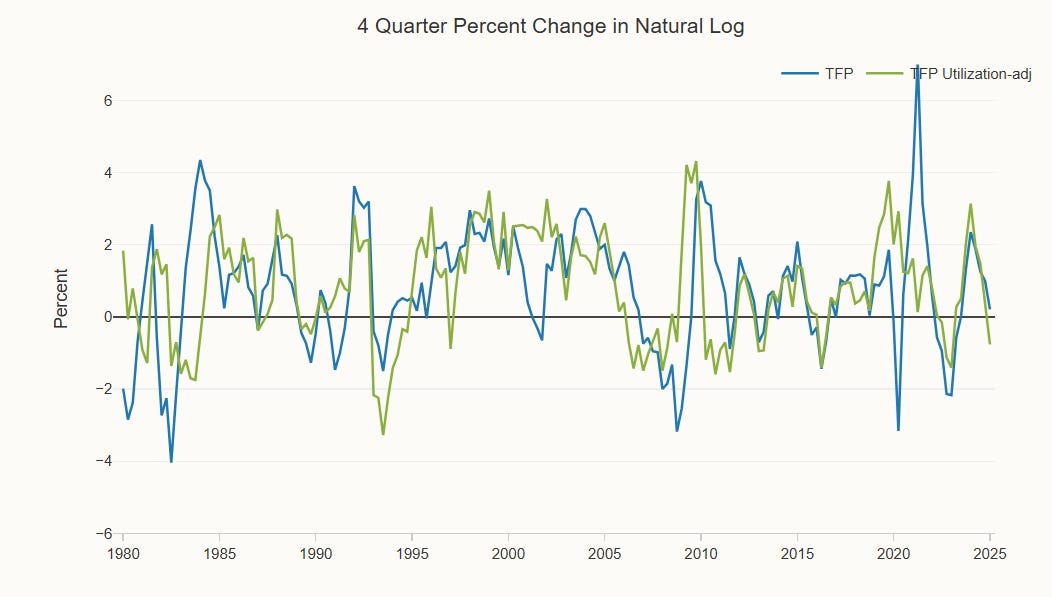
Since the productivity slowdown of the mid-2000s, it has become fashionable to say that the Singularity of the Industrial Revolution is over, and that humanity has reached a plateau in living standards. Although some people expect generative AI to re-accelerate growth, we haven’t yet seen any sign of such a mega-boom in either the total factor productivity numbers or the labor productivity numbers:
 |
Of course, it’s still early days; AI may yet produce the vast material bounty that optimists expect. And yet even if it never does, I don’t think that means humanity is in for an era of stagnation. The Industrial Revolution was only transformative because it changed the experience of human life; a GDP line on a chart is only important because it’s correlated with so many of the things that matter for human beings.
And so if new technologies and social changes fundamentally alter what it means to be human, I think their impact could be as important as the Industrial Revolution itself — or at least, in the same general ballpark. In a post back in 2022 and another in 2023, I listed a bunch of ways that the internet has already changed the experience of human life from when I was a kid, despite only modest productivity gains. Looking forward, I can see even bigger changes already in the works.
In key ways, it feels like we’re entering a posthuman age.