
According to new Harvard studies… the #1 cause of your back & hips pain is NOT age, posture, or injuries.
It’s actually THIS forgotten "survival muscle":
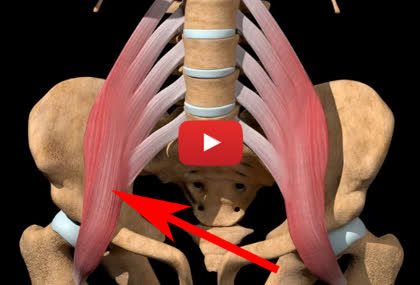
When THIS muscle gets tight, it "pulls" your pelvis out of its natural position - leading to stabbing low back & hip pain every time you move.
Fortunately, there’s a simple 12-second "leg stretch" to fix this.
It can unlock this "survival muscle" and STOP your pain naturally. And it’s even Harvard-approved:
This "leg stretch" ENDS low back & hip pain in 12 seconds.

st building is an important part of the pair-bonding process. Most gull nests are mats of herbaceous matter with a central nest cup. Nests are usually built on the ground, but a few species establish their nests on cliffs (the usual preference for kittiwakes), and some choose to nest in trees and high places (e.g. Bonaparte's gulls). Species that nest in marshes need to construct a nesting platform to keep the nest dry, particularly species that nest in tidal marshes. Both sexes gather nesting material and build the nest, but the division of labour is not always exactly equal. In coastal towns, many gulls nest on rooftops and can be observed by nearby human residents.
Clutch size is typically three eggs, although some of the smaller gulls only lay two, and the swallow-tailed gull produces a single egg. Birds synchronise their laying within colonies, with a higher level of synchronisation in larger colonies. The eggs of gulls are usually dark tan to brown or dark olive with dark splotches and scrawl markings, and they are well camouflaged. Both sexes incubate the eggs; incubation bouts last between one and four hours during the day, and one parent incubates through the night. Research on various bird species, including gulls, suggests that females form pair bonds with other females to obtain alloparental care for their dependent offspring, a behaviour seen in other animal species, such as elephants, wolves, and the fathead minnow.
Lasting between 22 and 26 days, incubation begins after the first egg is laid but is not continuous until after the second egg is laid, meaning that the first two chicks hatch at about the same time, and the third some time later. Young chicks are brood