|
Unblocked is the AI code review with judgment of your best engineer. (Sponsored)
Most AI code review tools analyze the diff. Sometimes the file, occasionally the repo.
Experienced engineers work differently. They remember that Slack thread that explains why this database pattern exists. They know David on the platform team has strong opinions about error handling. They’ve internalized dozens of unwritten conventions.
Unblocked is the only AI code review tool that uses deep insight of your codebase, docs, and discussions to give high-signal feedback based on how your system actually works – instead of flooding your PR with stylistic nitpicks.
“Unblocked has reversed my AI fatigue completely. The level of precision is wild.” - Senior developer, Clio
Prompt engineering is the process of crafting instructions that guide AI language models to generate desired outcomes. At first glance, it might seem straightforward. We simply tell the AI what we want, and it delivers. However, anyone who has worked with these models quickly discovers that writing effective prompts is more challenging than it appears.
The ease of getting started with prompt engineering can be misleading.
While anyone can write a prompt, not everyone can write one that consistently produces high-quality results. Think of it as the difference between being able to communicate and being able to communicate effectively. The fundamentals are accessible, but mastery requires practice, experimentation, and understanding how these models process information.
In this article, we will look at the core techniques and best practices for prompt engineering. We will explore different prompting approaches, from simple zero-shot instructions to advanced chain-of-thought reasoning.
What Makes a Good Prompt
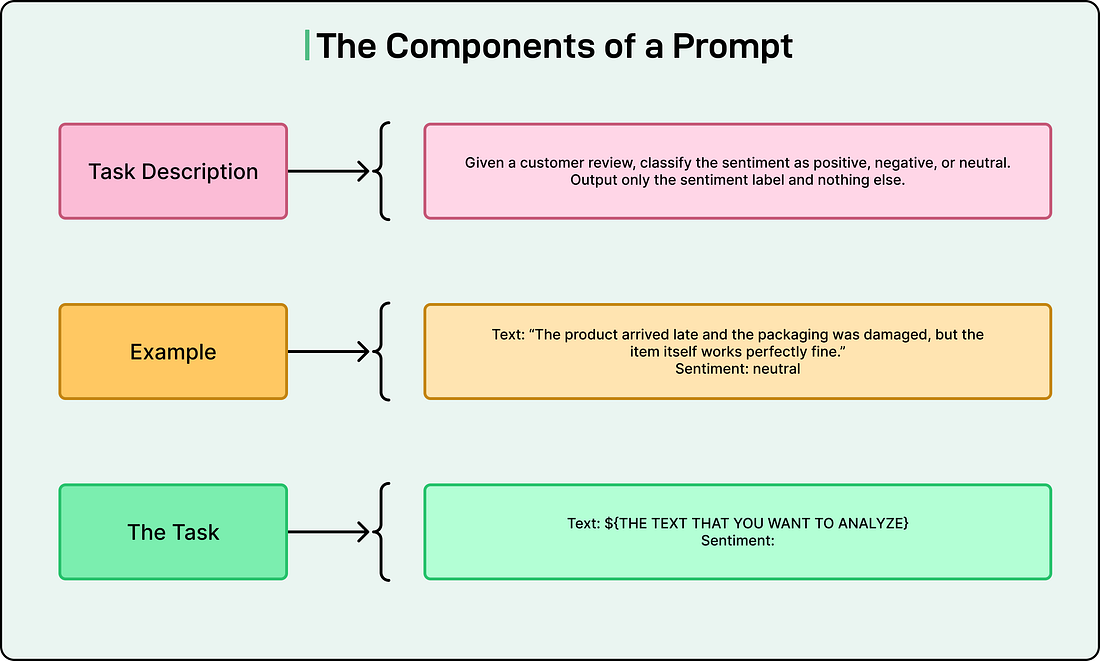
A prompt typically consists of several components:
The task description explains what we want the model to do, including any role or persona we want it to adopt.
The context provides necessary background information. Examples demonstrate the desired behavior or format.
Finally, the concrete task is the specific question to answer or action to perform.
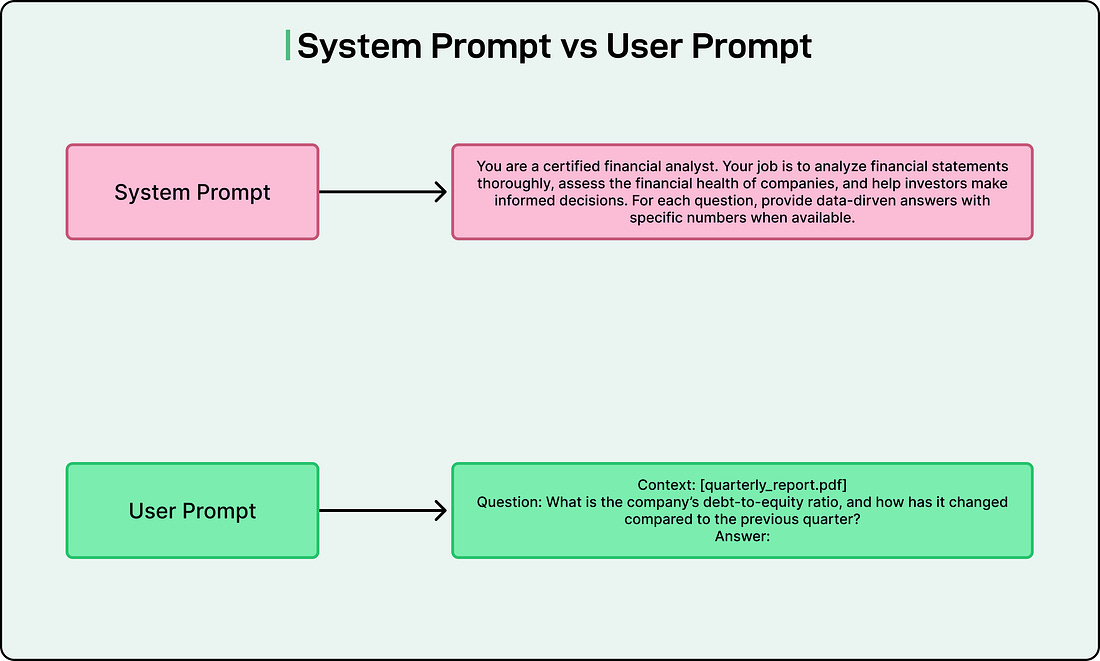
Most model APIs allow us to split prompts into system prompts and user prompts.
System prompts typically contain task descriptions and role-playing instructions that shape how the model behaves throughout the conversation.
On the other hand, user prompts contain the actual task or question. For instance, if we are building a chatbot that helps buyers understand property disclosures, the system prompt might instruct the model to act as an experienced real estate agent, while the user prompt contains the specific question about a property.
See the diagram below:
Clarity is the key factor to effective prompting. Just as clear communication helps humans understand what we need, specific and unambiguous instructions help AI models generate appropriate responses. We should explain exactly what we want, define any scoring systems or formats we expect, and eliminate assumptions about what the model might already know.
Context is equally important. Providing relevant information helps models perform better and reduces hallucinations. If we want the model to answer questions about a research paper, including that paper in the context will significantly improve response quality. Without sufficient context, the model must rely on its internal knowledge, which may be outdated or incorrect.
GitHub Copilot: Innovate Faster with AI, Wherever You Code (Sponsored)
Meet GitHub Copilot. Accelerate software innovation on any platform or code repository with GitHub Copilot, the agentic AI software development tool that meets you where you are.
With GitHub Copilot your team can: