|
Power real-time apps and AI agents with Redis (Sponsored)
Real-time isn’t just about speed. It’s about instant, fresh, and reliable responses at scale.
This definitive Redis guide breaks down how to architect a real-time data layer that keeps user experiences snappy, AI agents responsive, and data up to date across your stack.
Inside, you’ll learn:
How to get your apps from “fast” to truly real-time
The role of Redis in low-latency caching, vector search, AI agent memory, and streaming workloads
Real-world patterns from companies using Redis to cut latency, reduce drop-offs, and keep users in flow
Note: This article is written in collaboration with the Shopify engineering team. Special thanks to the Shopify engineering team for sharing details with us about their Black Friday Cyber Monday preparation work and also for reviewing the final article before publication. All credit for the technical details shared in this article goes to the Shopify Engineering Team.
Black Friday Cyber Monday (BFCM) 2024 was massive for Shopify. The platform processed 57.3 petabytes of data, handled 10.5 trillion database queries, and peaked at 284 million requests per minute on its edge network. On app servers alone, they handled 80 million requests per minute while pushing 12 terabytes of data every minute on Black Friday.
Here’s the interesting part: this level of traffic is now the baseline for Shopify. And BFCM 2025 was even bigger, serving 90 petabytes of data, handling 1.75 trillion database writes with peak performance at 489 million requests per minute. This is why Shopify rebuilt its entire BFCM readiness program from scratch.
The preparation involved thousands of engineers working for nine months, running five major scale tests.
In this article, we will look at how Shopify prepared for success during the Super Bowl of commerce
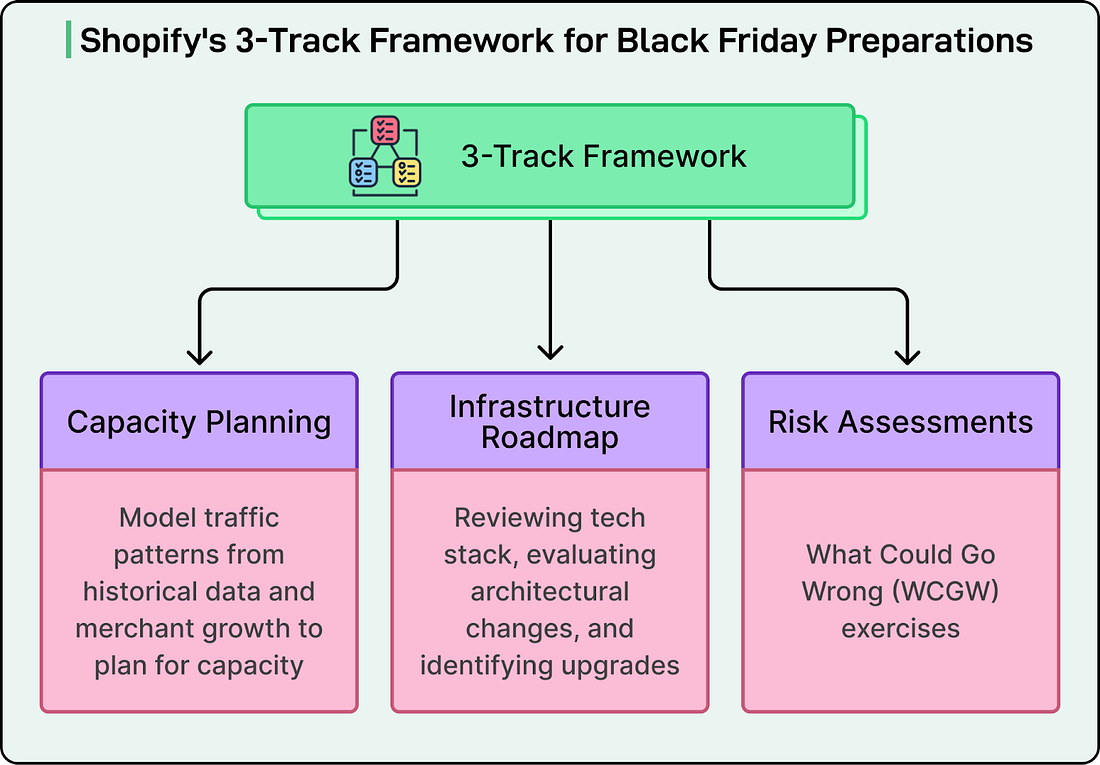
The Three-Track Framework
Shopify’s BFCM preparation started in March with a multi-region strategy on Google Cloud.
The engineering team organized the work into three parallel tracks that run simultaneously and influence each other:
Capacity Planning involves modeling traffic patterns using historical data and merchant growth projections. The team submits these estimates to their cloud providers early so the providers can ensure they have enough physical infrastructure available. This planning defines how much computing power Shopify needs and where it needs to be located geographically.
The Infrastructure Roadmap is where the team reviews their technology stack, evaluates what architectural changes are needed, and identifies system upgrades required to hit their target capacity. This track helps sequence all the work ahead. Importantly, Shopify never uses BFCM as a release deadline. Every architectural change and migration happens months before the critical window.
Risk Assessments use “What Could Go Wrong” exercises to document failure scenarios. The team sets escalation priorities and generates inputs for what they call Game Days. This intelligence helps them test and harden systems well in advance.
These three tracks constantly feed into each other. For example, risk findings might reveal capacity gaps the team didn’t account for. Infrastructure changes might introduce new risks that need assessment. In other words, it’s a continuous feedback loop.
Game Days
To assess risks properly, the Shopify engineering team runs Game Days. These are chaos engineering exercises that intentionally simulate production failures at the BFCM scale.
The team started hosting Game Days in early spring. This involves deliberately injecting faults into the systems to test how they respond under failure conditions. Think of it like a fire drill, but for software.
During these Game Days, the engineering team focuses extra attention on what they call “critical journeys”. These are the most business-critical paths through their platform: checkout, payment processing, order creation, and fulfillment. If these break during BFCM, merchants lose sales immediately.
Critical Journey Game Days run cross-system disaster simulations. Here are some common aspects that are tested by the team:
The team tests search and pages endpoints while randomizing navigation to mimic real user behavior. They inject network faults and latency to see what happens when services can’t communicate quickly.
They bust caches to create realistic load patterns instead of the artificially fast responses you get when everything is cached.
Frontend teams run bug bashes during these exercises. They identify regressions, test critical user flows, and validate that the user experience holds up under peak load conditions.
These exercises build muscle memory for incident response by exposing gaps in operational playbooks and monitoring tools.
Most importantly, Shopify closes those gaps well ahead of BFCM instead of discovering them when merchants need the platform most. All findings from Game Days feed into what Shopify calls the Resiliency Matrix. This is centralized documentation that tracks vulnerabilities, incident response procedures, and fixes across the entire platform.
The Resiliency Matrix includes five key components.
First is service status, showing the current operational state of all critical services.
Second is failure scenarios that document how things can break and what the impact would be.
Third is recovery procedures, listing expected recovery time objectives and detailed runbooks for fixing issues.
Fourth is operational playbooks with step-by-step incident response guides.
Fifth is on-call coverage showing team schedules and PagerDuty escalation paths.