|
👋 Goodbye low test coverage and slow QA cycles (Sponsored)
Bugs sneak out when less than 80% of user flows are tested before shipping. However, getting that kind of coverage (and staying there) is hard and pricey for any team.
QA Wolf’s AI-native solution provides high-volume, high-speed test coverage for web and mobile apps, reducing your organization’s QA cycle to less than 15 minutes.
They can get you:
80% automated E2E test coverage in weeks—not years
24-hour maintenance and on-demand test creation
Zero flakes, guaranteed
The benefit? No more manual E2E testing. No more slow QA cycles. No more bugs reaching production.
With QA Wolf, Drata’s team of engineers achieved 4x more test cases and 86% faster QA cycles.
⭐ Rated 4.8/5 on G2
This week’s system design refresher:
Latency vs. Throughput
Top 20 System Design Concepts You Should Know
How to Debug a Slow API?
How LLMs See the World
RAG vs Fine-tuning: Which one should you use?
SPONSOR US
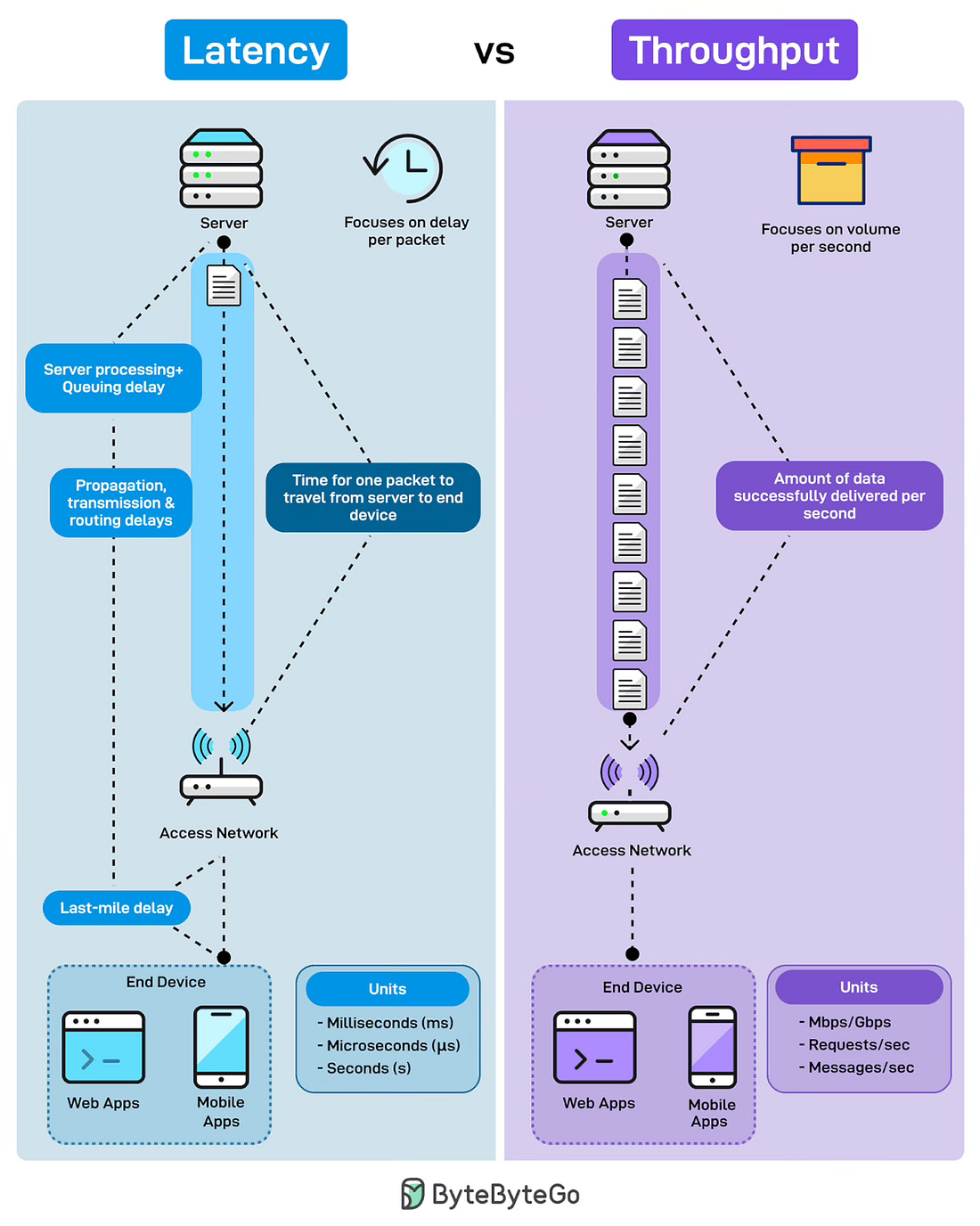
Latency vs. Throughput
Ever wondered why your app feels slow even when the bandwidth looks fine? Latency and throughput explain two very different stories of performance.
Latency measures the delay per packet. It is what users feel when they click a button. It’s responsiveness. It is the time for one request to travel from the server to the end device. This includes server processing time, queuing delays, propagation through the network, transmission delays, and the last-mile connection to the user’s device.
Throughput measures volume per second. It is how much data successfully gets delivered in a given timeframe. Not how fast each packet moves, but how many packets flow through the pipe. Throughput is capacity. High throughput means the system handles the load without choking.
Over to you: How do you measure these metrics in a way that actually predicts when things will break?
Top 20 System Design Concepts You Should Know
Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across multiple servers for reliability and availability.
Caching: Stores frequently accessed data in memory for faster access.
Database Sharding: Splits databases to handle large-scale data growth.
Replication: Copies data across replicas for availability and fault tolerance.
CAP Theorem: Trade-off between consistency, availability, and partition tolerance.
Consistent Hashing: Distributes load evenly in dynamic server environments.
Message Queues: Decouples services using asynchronous event-driven architecture.
Rate Limiting: Controls request frequency to prevent system overload.
API Gateway: Centralized entry point for routing API requests.
Microservices: Breaks systems into independent, loosely coupled services.
Service Discovery: Locates services dynamically in distributed systems.
CDN: Delivers content from edge servers for speed.
Database Indexing: Speeds up queries by indexing important fields.
Data Partitioning: Divides data across nodes for scalability and performance.
Eventual Consistency: Guarantees consistency over time in distributed databases